Inclusions in Burmese Amber

Burmese amber has been well documented in the paleontological literature, but is overshadowed in the gemological community by material from the Dominican Republic and the Baltic area. Despite the armed conflict in the Hukawng Valley, possibly the world’s largest tiger reserve, accessibility has improved and amber production has steadily increased since 2014. As a result, more Burmese amber is reaching the marketplace. We have observed rising interest in the Bangkok, China, and Hong Kong markets, with specimens containing large inclusions of flora and fauna in great demand and commanding high prices. The samples presented here (figures 1–3) were acquired during a January 2016 field expedition to the Hukawng Valley and are now part of the GIA research collection.

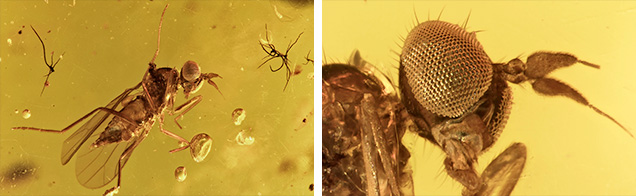
Figure 3. Left: The delicate features of this fly, particularly its wings, are surrounded by gas bubbles and trichomes (hair-like structures that grow on plants). Right: This image demonstrates the excellent preservation qualities of amber, as evidenced by the detailed structure of the fly’s eye. Photomicrographs by Victoria Raynaud; field of view 4.80 mm (left) and 0.86 mm (right). Brightfield and fiber-optic illumination.
These amber specimens are interesting because they potentially preserve evidence from biological environments of 80 to 100 million years ago (G. Shi et al., “Age constraint on Burmese amber based on U–Pb dating of zircons,” Cretaceous Research, Vol. 37, 2012, pp. 155–163, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0195667112000535). They are significantly older than amber from the Dominican Republic, estimated at 25–40 million years old) and the Baltic region, which are about 25–28 million years old (D. Penney, Biodiversity of Fossils in Amber from the Major World Deposits, Siri Scientific Press, Manchester, United Kingdom, 2010).



